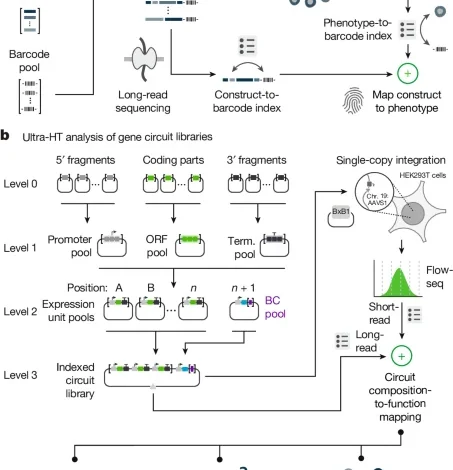
Ultra-high-throughput mapping of genetic design space
de Boer, C. G. et al. Deciphering eukaryotic gene-regulatory logic with 100 million random promoters. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 56–65 (2020).
Google Scholar
Castillo-Hair, S. et al. Optimizing 5′UTRs for mRNA-delivered gene editing using deep learning. Nat. Commun. 15, 5284 (2024).
Google Scholar
Angenent-Mari, N. M., Garruss, A. S., Soenksen, L. R., Church, G. & Collins, J. J. A deep learning approach to programmable RNA switches. Nat. Commun. 11, 5057 (2020).
Google Scholar
Sahu, B. et al. Sequence determinants of human gene regulatory elements. Nat. Genet. 54, 283–294 (2022).
Google Scholar
Jones, E. M. et al. Structural and functional characterization of G protein-coupled receptors with deep mutational scanning. eLife 9, e54895 (2020).
Google Scholar
Zhang, C., Tsoi, R. & You, L. Addressing biological uncertainties in engineering gene circuits. Integr. Biol. 8, 456–464 (2016).
Google Scholar
Kitano, S., Lin, C., Foo, J. L. & Chang, M. W. Synthetic biology: learning the way toward high-precision biological design. PLoS Biol. 21, e3002116 (2023).
Google Scholar
English, M. A., Gayet, R. V. & Collins, J. J. Designing biological circuits: synthetic biology within the operon model and beyond. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 90, 221–244 (2021).
Google Scholar
Mahata, B. et al. Compact engineered human mechanosensitive transactivation modules enable potent and versatile synthetic transcriptional control. Nature Methods 20, 1716–1728 (2023).
Slusarczyk, A. L., Lin, A. & Weiss, R. Foundations for the design and implementation of synthetic genetic circuits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 406–420 (2012).
Google Scholar
Bashor, C. J. & Collins, J. J. Understanding biological regulation through synthetic biology. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 47, 399–423 (2018).
Google Scholar
Bashor, C. J., Hilton, I. B., Bandukwala, H., Smith, D. M. & Veiseh, O. Engineering the next generation of cell-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 21, 655–675 (2022).
Google Scholar
Beitz, A. M., Oakes, C. G. & Galloway, K. E. Synthetic gene circuits as tools for drug discovery. Trends Biotechnol. 40, 210–225 (2022).
Google Scholar
Kitada, T., DiAndreth, B., Teague, B. & Weiss, R. Programming gene and engineered-cell therapies with synthetic biology. Science 359, eaad1067 (2018).
Google Scholar
Cameron, D. E., Bashor, C. J. & Collins, J. J. A brief history of synthetic biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 12, 381–390 (2014).
Google Scholar
Yeung, E. et al. Biophysical constraints arising from compositional context in synthetic gene networks. Cell Syst. 5, 11–24 (2017).
Google Scholar
Lou, C., Stanton, B., Chen, Y. J., Munsky, B. & Voigt, C. A. Ribozyme-based insulator parts buffer synthetic circuits from genetic context. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 1137–1142 (2012).
Google Scholar
Muller, I. E. et al. Gene networks that compensate for crosstalk with crosstalk. Nat. Commun. 10, 4028 (2019).
Google Scholar
Kinney, J. B., Murugan, A., Callan, C. G. Jr. & Cox, E. C. Using deep sequencing to characterize the biophysical mechanism of a transcriptional regulatory sequence. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 9158–9163 (2010).
Google Scholar
Sharon, E. et al. Inferring gene regulatory logic from high-throughput measurements of thousands of systematically designed promoters. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 521–530 (2012).
Google Scholar
Kosuri, S. et al. Composability of regulatory sequences controlling transcription and translation in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 14024–14029 (2013).
Google Scholar
Taskiran, I. I. et al. Cell-type-directed design of synthetic enhancers. Nature 626, 212–220 (2024).
Google Scholar
Gosai, S. J. et al. Machine-guided design of cell-type-targeting cis-regulatory elements. Nature 634, 1211–1220 (2024).
Google Scholar
Agarwal, V. et al. Massively parallel characterization of transcriptional regulatory elements. Nature 639, 411–420 (2025).
Google Scholar
Bogard, N., Linder, J., Rosenberg, A. B. & Seelig, G. A deep neural network for predicting and engineering alternative polyadenylation. Cell 178, 91–106 (2019).
Google Scholar
Khoroshkin, M. et al. A generative framework for enhanced cell-type specificity in rationally designed mRNAs. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.31.630783 (2024).
Gera, T., Jonas, F., More, R. & Barkai, N. Evolution of binding preferences among whole-genome duplicated transcription factors. eLife 11, e73225 (2022).
Google Scholar
DelRosso, N. et al. Large-scale mapping and mutagenesis of human transcriptional effector domains. Nature 616, 365–372 (2023).
Zhou, Y. et al. Encoding genetic circuits with DNA barcodes paves the way for machine learning-assisted metabolite biosensor response curve profiling in yeast. ACS Synth. Biol. 11, 977–989 (2022).
Google Scholar
Wong, A. S., Choi, G. C., Cheng, A. A., Purcell, O. & Lu, T. K. Massively parallel high-order combinatorial genetics in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 952–961 (2015).
Google Scholar
Matreyek, K. A. et al. Multiplex assessment of protein variant abundance by massively parallel sequencing. Nat. Genet. 50, 874–882 (2018).
Google Scholar
Liu, H. et al. Magic pools: parallel assessment of transposon delivery vectors in bacteria. mSystems 3, e00143-17 (2018).
Google Scholar
Weber, E., Engler, C., Gruetzner, R., Werner, S. & Marillonnet, S. A modular cloning system for standardized assembly of multigene constructs. PLoS ONE 6, e16765 (2011).
Google Scholar
Duportet, X. et al. A platform for rapid prototyping of synthetic gene networks in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 13440–13451 (2014).
Google Scholar
Petitclerc, D. et al. The effect of various introns and transcription terminators on the efficiency of expression vectors in various cultured cell lines and in the mammary gland of transgenic mice. J. Biotechnol. 40, 169–178 (1995).
Google Scholar
Khalil, A. S. et al. A synthetic biology framework for programming eukaryotic transcription functions. Cell 150, 647–658 (2012).
Google Scholar
Maeder, M. L., Thibodeau-Beganny, S., Sander, J. D., Voytas, D. F. & Joung, J. K. Oligomerized pool engineering (OPEN): an ‘open-source’ protocol for making customized zinc-finger arrays. Nat. Protoc. 4, 1471–1501 (2009).
Google Scholar
Li, H. S. et al. Multidimensional control of therapeutic human cell function with synthetic gene circuits. Science 378, 1227–1234 (2022).
Google Scholar
Feil, R., Wagner, J., Metzger, D. & Chambon, P. Regulation of Cre recombinase activity by mutated estrogen receptor ligand-binding domains. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 237, 752–757 (1997).
Google Scholar
Bashor, C. J. et al. Complex signal processing in synthetic gene circuits using cooperative regulatory assemblies. Science 364, 593–597 (2019).
Google Scholar
Donahue, P. S. et al. The COMET toolkit for composing customizable genetic programs in mammalian cells. Nat. Commun. 11, 779 (2020).
Google Scholar
Muldoon, J. J. et al. Model-guided design of mammalian genetic programs. Sci. Adv. 7, eabe9375 (2021).
Google Scholar
Kabadi, A. M. & Gersbach, C. A. Engineering synthetic TALE and CRISPR/Cas9 transcription factors for regulating gene expression. Methods 69, 188–197 (2014).
Google Scholar
La Russa, M. F. & Qi, L. S. The new state of the art: Cas9 for gene activation and repression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 35, 3800–3809 (2015).
Google Scholar
Sadowski, I., Ma, J., Triezenberg, S. & Ptashne, M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature 335, 563–564 (1988).
Google Scholar
Shin, Y. et al. Spatiotemporal control of intracellular phase transitions using light-activated optoDroplets. Cell 168, 159–171 (2017).
Google Scholar
Schneider, N. et al. Liquid-liquid phase separation of light-inducible transcription factors increases transcription activation in mammalian cells and mice. Sci. Adv. 7, eabd3568 (2021).
Google Scholar
Gossen, M. & Bujard, H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5547–5551 (1992).
Google Scholar
Shin, Y. & Brangwynne, C. P. Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science 357, eaaf4382 (2017).
Google Scholar
Tycko, J. et al. Development of compact transcriptional effectors using high-throughput measurements in diverse contexts. Nat. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02442-6 (2024).
Google Scholar
Tague, E. P., Dotson, H. L., Tunney, S. N., Sloas, D. C. & Ngo, J. T. Chemogenetic control of gene expression and cell signaling with antiviral drugs. Nat. Methods 15, 519–522 (2018).
Google Scholar
Jiang, K. et al. Rapid in silico directed evolution by a protein language model with EVOLVEpro. Science 387, eadr6006 (2025).
Google Scholar
Lin, J., Luo, R. & Pinello, L. EPInformer: a scalable deep learning framework for gene expression prediction by integrating promoter-enhancer sequences with multimodal epigenomic data. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.08.01.606099 (2024).
Wimmer, E., Mueller, S., Tumpey, T. M. & Taubenberger, J. K. Synthetic viruses: a new opportunity to understand and prevent viral disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 27, 1163–1172 (2009).
Google Scholar
Brophy, J. A. & Voigt, C. A. Principles of genetic circuit design. Nat. Methods 11, 508–520 (2014).
Google Scholar
Pinglay, S. et al. Synthetic regulatory reconstitution reveals principles of mammalian Hox cluster regulation. Science 377, eabk2820 (2022).
Google Scholar
Voigt, C. A. Synthetic biology 2020-2030: six commercially-available products that are changing our world. Nat. Commun. 11, 6379 (2020).
Google Scholar
Valeri, J. A. et al. Sequence-to-function deep learning frameworks for engineered riboregulators. Nat. Commun. 11, 5058 (2020).
Google Scholar
Hollerer, S. et al. Large-scale DNA-based phenotypic recording and deep learning enable highly accurate sequence-function mapping. Nat. Commun. 11, 3551 (2020).
Google Scholar
Rai, K., Wang, Y., O’Connell, R. W., Patel, A. B. & Bashor, C. J. Using machine learning to enhance and accelerate synthetic biology. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 31, 100553 (2024).
Karst, S. M. et al. High-accuracy long-read amplicon sequences using unique molecular identifiers with Nanopore or PacBio sequencing. Nat. Methods 18, 165–169 (2021).
Google Scholar
Chung, C. T., Niemela, S. L. & Miller, R. H. One-step preparation of competent Escherichia coli: transformation and storage of bacterial cells in the same solution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 2172–2175 (1989).
Google Scholar
Parrish, J. R. et al. High-throughput cloning of Campylobacter jejuni ORfs by in vivo recombination in Escherichia coli. J. Proteome Res. 3, 582–586 (2004).
Google Scholar
Currin, A. et al. Highly multiplexed, fast and accurate nanopore sequencing for verification of synthetic DNA constructs and sequence libraries. Synth. Biol. 4, ysz025 (2019).
Google Scholar
De Coster, W., Weissensteiner, M. H. & Sedlazeck, F. J. Towards population-scale long-read sequencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 22, 572–587 (2021).
Google Scholar
Smith, T. F. & Waterman, M. S. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J. Mol. Biol. 147, 195–197 (1981).
Google Scholar
Cong, L. et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339, 819–823 (2013).
Google Scholar
Hermann, M. et al. Binary recombinase systems for high-resolution conditional mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 3894–3907 (2014).
Google Scholar